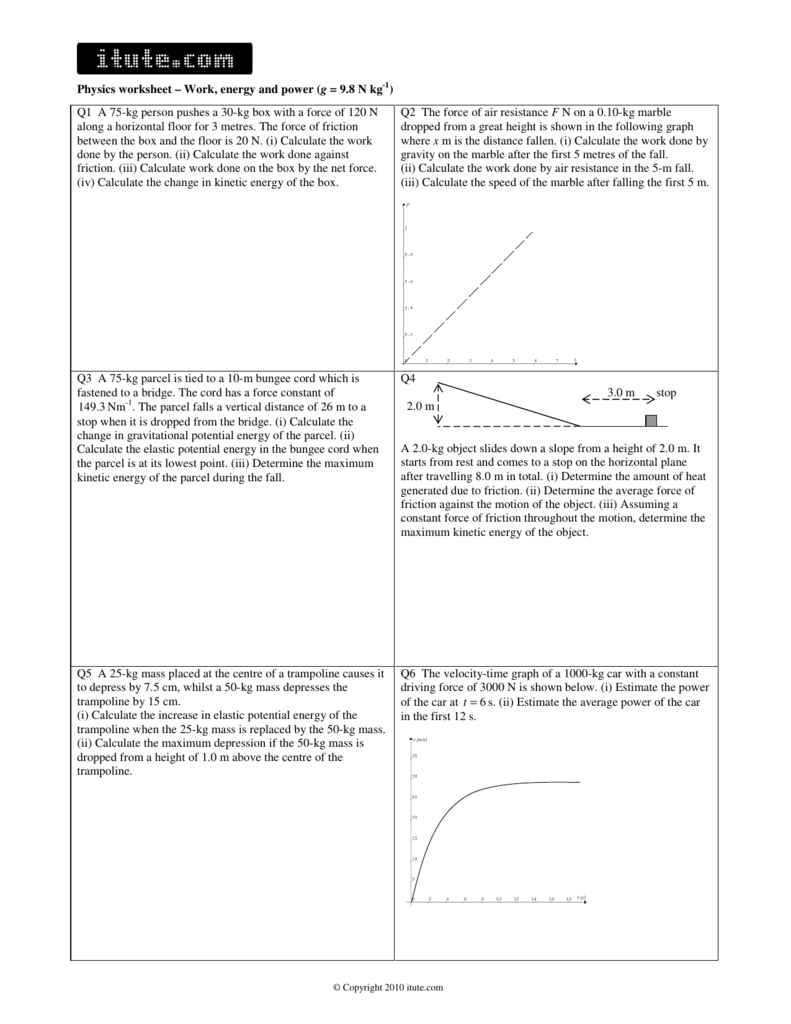
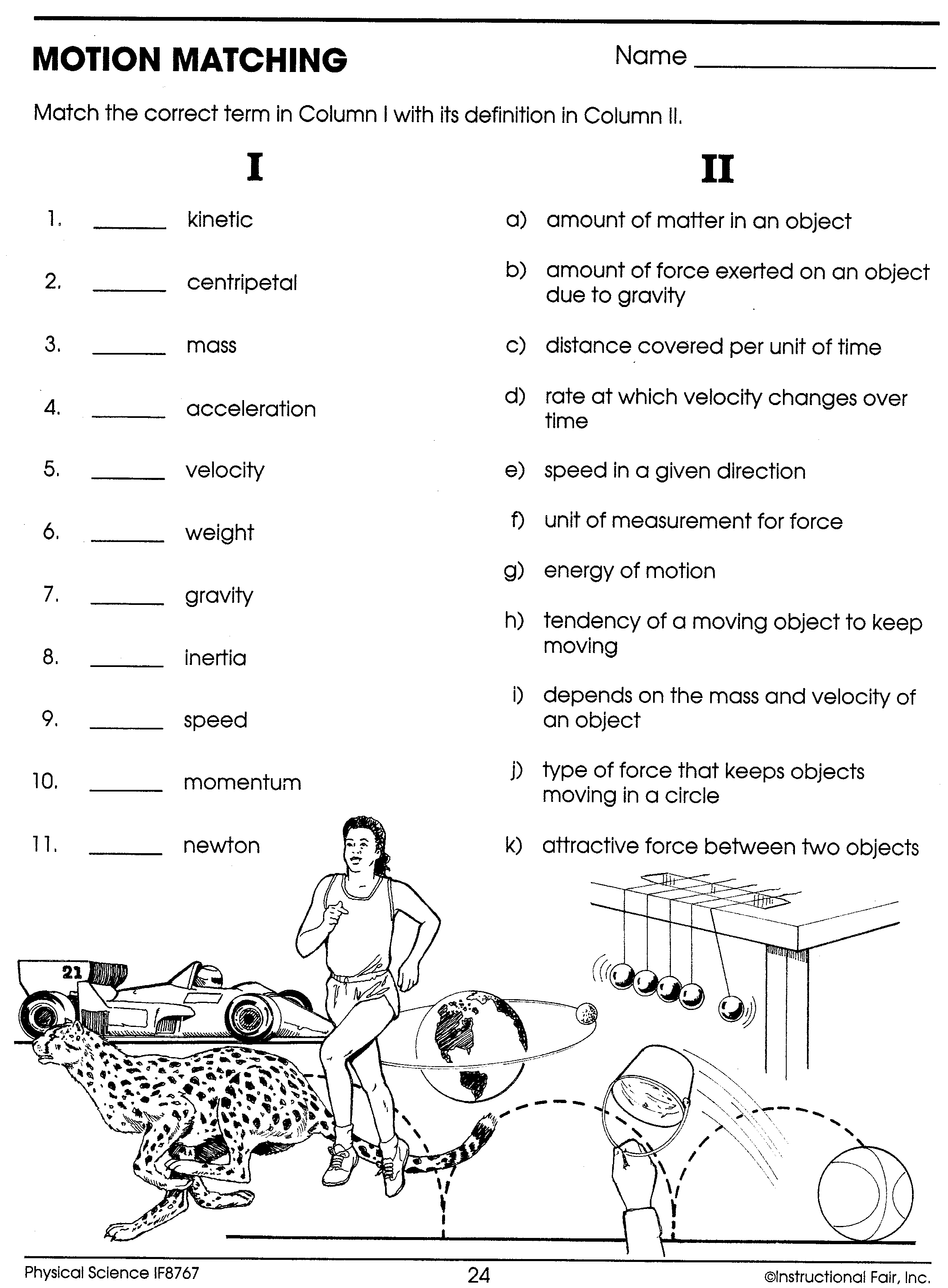
Work Power Energy Worksheet - Work and power problems 1) how much work will you do if you push a block of concrete 4.3 m along a floor with a steady force of 25 n? Work (1 mark questions) 1. When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____. _____ is the rate at which work is done. An artificial satellite is at a height of 36,500km above earth’s surface. Calculate the work done by a. Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. Work, power and energy worksheet name l. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. Calculate the work done by a 47 n force pushing a pencil 0.26 m.
Work and power problems 1) how much work will you do if you push a block of concrete 4.3 m along a floor with a steady force of 25 n? Work, power and energy worksheet name l. Work (1 mark questions) 1. Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. Calculate the work done by a 47 n force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. _____ is the rate at which work is done. An artificial satellite is at a height of 36,500km above earth’s surface. When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____. Calculate the work done by a.
These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. _____ is the rate at which work is done. When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____. An artificial satellite is at a height of 36,500km above earth’s surface. Work (1 mark questions) 1. Calculate the work done by a 47 n force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. Work and power problems 1) how much work will you do if you push a block of concrete 4.3 m along a floor with a steady force of 25 n? Work, power and energy worksheet name l. Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. Calculate the work done by a.
Work And Energy Physics Worksheet Martin Lindelof
Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. Calculate the work done by a 47 n force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. Work, power and energy worksheet name l. Work (1 mark questions) 1. When calculating power, you should use the formula.
Work Energy And Power Worksheets
An artificial satellite is at a height of 36,500km above earth’s surface. Calculate the work done by a. Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. Work and power problems 1) how much work will you do if you push a block.
15 Physics Work Energy And Power Worksheet Free PDF at
Work and power problems 1) how much work will you do if you push a block of concrete 4.3 m along a floor with a steady force of 25 n? An artificial satellite is at a height of 36,500km above earth’s surface. Work (1 mark questions) 1. When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by.
Physics 11 Work Power Energy Worksheet Worksheets For Kindergarten
Work, power and energy worksheet name l. Work (1 mark questions) 1. Calculate the work done by a 47 n force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. _____ is the rate at which work is done. When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____.
Physics 11 Work Power Energy Worksheet Printable Worksheets And
Calculate the work done by a 47 n force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. Calculate the work done by a. Work and power problems 1) how much work will you do if you push a block of concrete 4.3 m along a floor with a steady force of 25.
Worksheet Work Power And Energy
Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. Calculate the work done by a. _____ is the rate at which work is done. An artificial satellite is at a height of.
Work And Power Physics Worksheet
_____ is the rate at which work is done. Work (1 mark questions) 1. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. Work, power and energy worksheet name l. Work and power problems 1) how much work will you do if you push a block of concrete 4.3 m along a floor with a steady force of.
Physics 11 Work Power Energy Worksheet Worksheets For Kindergarten
Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. Work (1 mark questions) 1. _____ is the rate at which work is done. Calculate the work done by a 47 n force.
Work and Power Practice WS Solutions Regents Physics Worksheets
Calculate the work done by a 47 n force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. Work, power and energy worksheet name l. Calculate the work done by a. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a.
Free Collection of Work, Power, and Energy Worksheets
Work (1 mark questions) 1. _____ is the rate at which work is done. Work, power and energy worksheet name l. Work and power problems 1) how much work will you do if you push a block of concrete 4.3 m along a floor with a steady force of 25 n? An artificial satellite is at a height of 36,500km.
An Artificial Satellite Is At A Height Of 36,500Km Above Earth’s Surface.
Work and power problems 1) how much work will you do if you push a block of concrete 4.3 m along a floor with a steady force of 25 n? _____ is the rate at which work is done. Work, power and energy worksheet name l. Calculate the work done by a 47 n force pushing a pencil 0.26 m.
These Problem Sets Focus On The Use Of Energy Principles To.
Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. Calculate the work done by a. Work (1 mark questions) 1. When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____.